Ethical Hacking
How to Hack WiFi (Wireless) Network
Wireless networks are accessible to anyone within the router’s transmission radius. This makes...
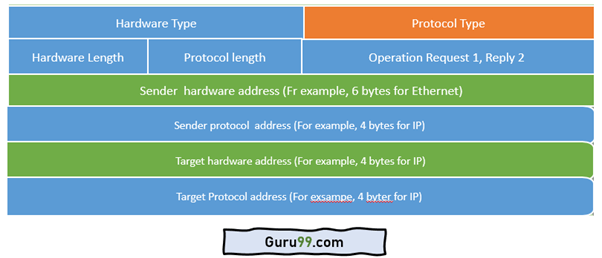
Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is an important protocol of the network layer in the OSI model, which helps find the MAC (Media Access Control) address given the system's IP address. The ARP's main task is to convert the 32-bit IP address (for IPv4) to a 48-bit MAC address.
This protocol is mostly used to determine the hardware (MAC) address of a device from an IP address. It is also used when one device wants to communicate with some other device on a local network. The full form of ARP is Address Resolution Protocol.
In this networking tutorial, you will learn:
All OS in an IPv4 network keep an ARP cache. When the host requests a MAC address to send a packet to another host in the LAN, it checks its ARP cache to check that the MAC address translation already presents.
Let us understand this concept with an example:
Association between a protocol address and a hardware address is known as binding.
There are three techniques used for this purpose:
Here are four types of Address Resolution Protocol, which is given below:
Let us learn them all in detail:
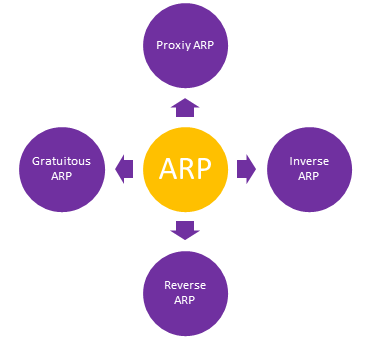
In the Proxy ARP method, Layer 3 devices can respond to ARP requests. This ARP type is configured router will respond to the target IP address and maps the router's MAC address with the target IP address and sender when it is reached to its destination.
Gratuitous is another type of ARP request of the host. This type of ARP request helps the network to identify the duplicate IP address. Therefore, when an ARP request is sent by a router or switch to get its IP address, no ARP responses are received. So that no other nodes can use the IP address allocated to that switch or router.
Reverse ARP, also now called RARP, is a type of ARP networking protocol which is used by the client system in a LAN to request its IPv4 address from the ARP router table. The network admin mostly creates a table in the gateway-router, which helps determine the MAC address to that specific IP address.
Inverse ARP is also called InARP, is a type of ARP used to find the nodes' IP of addresses from the data link layer addresses. InARP is widely used for ATM networks frame relays where Layer 2 virtual circuit addressing acquired from Layer 2 signaling.
Here are the pros/benefits of using ARP
What happens if an ARP request is made for a non-existing host?
If the several ARP requests are made for a non-existing host, it will increase time intervals between requests. Eventually, ARP gives up.
What if a host sends an ARP request for its IP address?
The other machines respond (gratuitous ARP) as a normal ARP request. This helps to detect an IP address has already been assigned.
Wireless networks are accessible to anyone within the router’s transmission radius. This makes...
Anti-spyware removes malicious spyware and protects your computer system. They detect and remove...
What is CISSP? CISSP- full form Certified Information Systems Security Professional is considered as a...
What is Digital Forensics? Digital Forensics is defined as the process of preservation,...
What is Cybercrime? Cybercrime is defined as an unlawful action against any person using a...
Training Summary An Ethical Hacker exposes vulnerabilities in software to help business owners fix...