SDLC
Difference between Website and Web Application
What is a Website? A website is a group of globally accessible, interlinked web pages which have a...
Continuous integration is a software development method where members of the team can integrate their work at least once a day. In this method, every integration is checked by an automated build to search the error. The CI concept was first introduced over two decades ago to avoid "integration hell," which happens when integration is put off till the end of a project.
In Continuous Integration after a code commit, the software is built and tested immediately. In a large project with many developers, commits are made many times during a day. With each commit code is built and tested. If the test is passed, build is tested for deployment. If the deployment is a success, the code is pushed to Production. This commit, build, test, and deploy is a continuous process, and hence the name continuous integration/deployment.
In this CI tutorial, you will learn:
Here are key differences between development using CI or without CI.
| Development without CI | Development with CI |
| Lots of Bugs | Fewer bugs |
| Infrequent commits | Regular commits |
| Infrequent and slow releases | Regular working releases |
| Difficult integration | Easy and Effective Integration |
| Testing happens late | Testing happens early and often. |
| Issue raised are harder to fix | Find and fix problems faster and more efficiently. |
| Poor project visibility | Better project visibility |
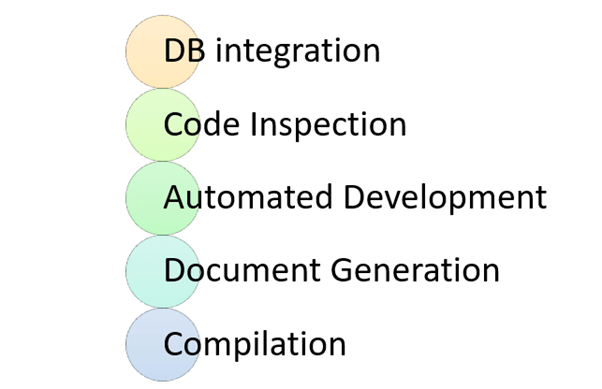
While compilation only compiles a code, CI does the following activities
DB integration:
Code Inspection:
Automated Deployment:
Document generation:
Compilation:
Compilation is the process the computer takes to convert a high-level programming language code into a machine language that the computer able to understand. It ensures a code compiler on every target platform.
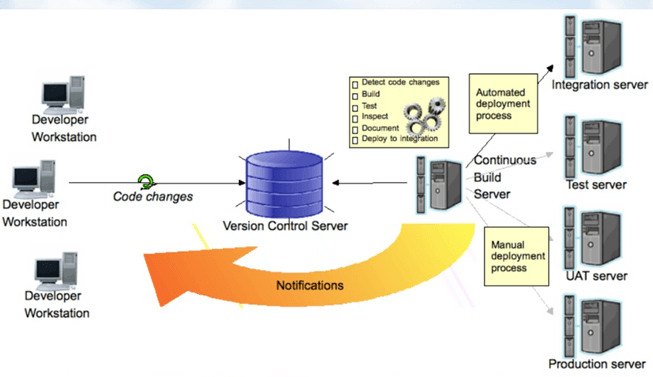
Here, are the key elements which you need to perfom the entire CI process:
You are surely aware of the old phone Nokia. Nokia used to implement a procedure called nightly build. After multiple commits from diverse developers during the day, the software built every night. Since the software was built only once in a day, it's a huge pain to isolate, identify, and fix the errors in a large codebase.
Later, they adopted the Continuous Integration approach. The software was built and tested as soon as a developer committed code. If any error is detected, the respective developer can quickly fix the defect.
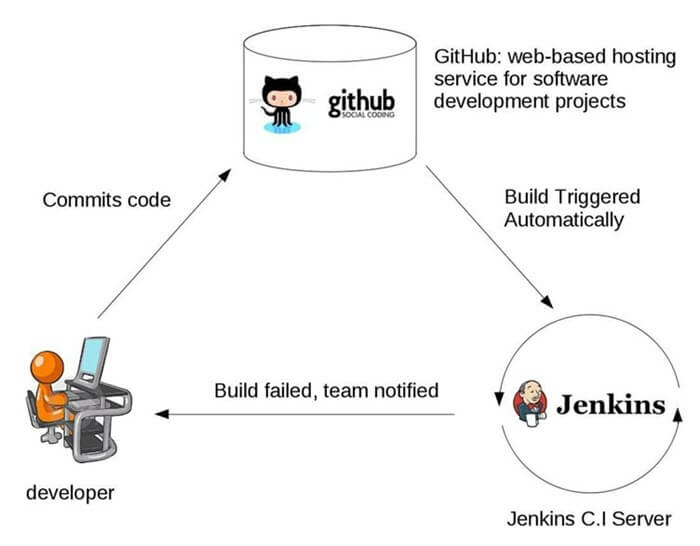
Here, are important features of Continuous Integration
Here are important reasons for using Continuous Integration:
Here, are some important best practices while implementing
Here, are cons/drawbacks of Continuous Integration process:
Here, are some most essential CI tools:
Jenkins is an open-source continuous integration tool. It is written using the Java programming language. It facilitates real-time testing and reporting on isolated changes in a more massive codebase. This software helps developers to quickly find and solve defects in their codebase & automate testing of their builds.
Bamboo is a continuous integration build server that performs - automatic build, test, and releases in a single place. It works seamlessly with JIRA software and Bitbucket. Bamboo supports many languages and technologies such as CodeDeply, Ducker, Git, SVN, Mercurial, AWS, and Amazon S3 buckets.
TeamCity is a Continuous Integration server that supports many powerful features. It maintains a CI server healthy and stable even when no builds are running. It provides better code quality for any project
What is a Website? A website is a group of globally accessible, interlinked web pages which have a...
1) What is ServiceNow? ServiceNow is a cloud-based IT Service Management tool. It offers a single...
What is TCL? TCL is shell application that reads TCL command from its standard input or from a...
Software engineering is defined as a process of analyzing user requirements and then designing,...
What is Full Stack Developer? Full Stack Developer is an engineer who works on both client-side and...
C++ Tutorial Summary To learn C++ programming, refer to these tutorials in the given order. This...