BigData
Big Data Testing Tutorial: What is, Strategy, How to test Hadoop
Big Data Testing Big Data Testing is a testing process of a big data application in order to...
The do-while loop iterates a section of the C++ program several times. In the do-while loop, test expression is added at the bottom of the loop. The loop body comes before the test expression. That's why the loop body must execute for once, even when test expression evaluates to false in the first test.
In this C++ tutorial, you will learn:
The do-while loop should be used when the number of iterations is not fixed, and the loop must execute for at least once. The C++ compiler executes the loop body first before evaluating the condition. That means the loop must return a result. This is the case even when the test condition evaluates to a false on the first evaluation. Since the loop body has already been executed, it must return the result.
The basic syntax of C++ do while loop is as follows:
do{
//code
}while(condition);
The condition is test expression. It must be true for the loop to execute. The { and } mark the body of do while loop. It comes before the condition. Hence, it is executed before the condition.
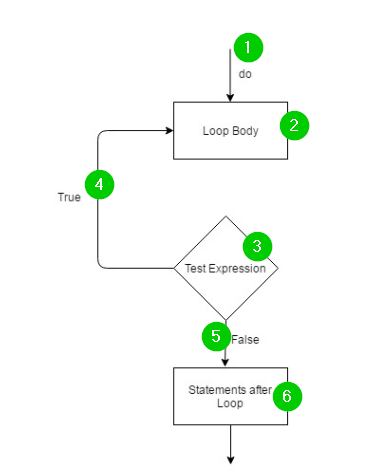
Flow Chart Explanation:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Local variable
int x = 1;
do {
cout << "X is: " << x << endl;
x = x + 1;
} while (x < 5);
return 0;
}
Output:
Here is a screenshot of the code:
Code Explanation:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int num, sum = 0;
do {
cout << "Enter a number: ";
cin >> num;
sum += num;
} while (num != 0);
cout << "Sum is " << sum;
return 0;
}
Output:
Here is a screenshot of the code:
Code Explanation:
In C++, it is possible for us to create one do-while loop inside another do-whole loop. This results into a nested do-while loop.
do{
statement(s)
do{
statement(s)
}while(condition);
statement(s)
}while(condition);
The first do statement denotes the do part of the outer do-while loop.
The second do statement denotes the do part of the inner do-while loop.
The first while statement denotes the test condition for the inner loop.
The second while statement denotes the test condition for the outer loop.
Nested do while loop works as follows:
Step 1: The initialization is executed first and once.
Step 2: The statements (the do) is executed once.
Step 3: Test expression is evaluation by flow control.
Step 4: If true, inner loop is executed.
Step 5: Updating statement(s) are updated.
Step 6: Process runs repeatedly until test expression becomes false.
Step 7: When test expression becomes false, inner loop is exited and control jumps to outer loop.
Step 8: Test condition is evaluated again.
Step 9: If true, statement(s) are executed to return false.
Step 10: Execution of loop stops and control jumps to statements after loop.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 1;
do {
int b = 1;
do {
cout << a << "\n";
b++;
} while (b <= 3);
a++;
} while (a <= 3);
}
Output:
Here is a screenshot of the code:
Code Explanation:
Big Data Testing Big Data Testing is a testing process of a big data application in order to...
Download PDF 1) What are the important categories of software? System software Application...
$20.20 $9.99 for today 4.6 (125 ratings) Key Highlights of R Programming Tutorial PDF 383+ pages...
Slideshow maker software are applications used to develop presentations or videos with different...
Video grabbers are tools to store videos in numerous formats, including MP3 and MP4. These...
In data analysis you can sort your data according to a certain variable in the dataset. In R, we...