PL-SQL
PL/SQL Tutorial PDF: Oracle SQL for Beginners (Download Now)
$20.20 $9.99 for today 4.5 (108 ratings) Key Highlights of PL/SQL Tutorial PDF 188+ pages eBook...
Normalization is a database design technique that reduces data redundancy and eliminates undesirable characteristics like Insertion, Update and Deletion Anomalies. Normalization rules divides larger tables into smaller tables and links them using relationships. The purpose of Normalization in SQL is to eliminate redundant (repetitive) data and ensure data is stored logically.
The inventor of the relational model Edgar Codd proposed the theory of normalization of data with the introduction of the First Normal Form, and he continued to extend theory with Second and Third Normal Form. Later he joined Raymond F. Boyce to develop the theory of Boyce-Codd Normal Form.
Here is a list of Normal Forms
The Theory of Data Normalization in SQL server is still being developed further. For example, there are discussions even on 6th Normal Form. However, in most practical applications, normalization achieves its best in 3rd Normal Form. The evolution of SQL Normalization theories is illustrated below-
.png)
Database Normalization Example can be easily understood with the help of a case study. Assume, a video library maintains a database of movies rented out. Without any normalization in database, all information is stored in one table as shown below. Let's understand Normalization in database with tables example:
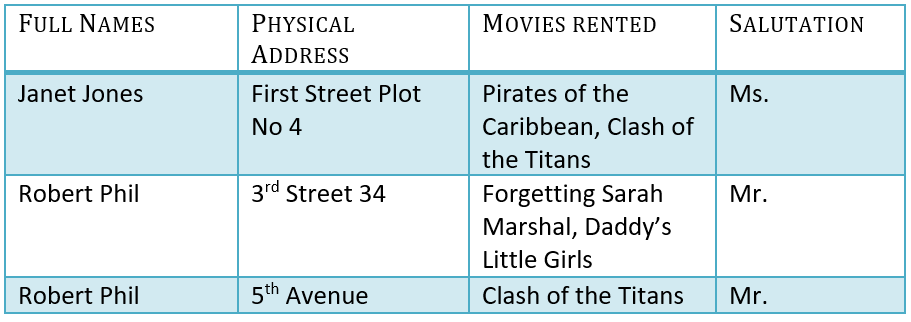
Here you see Movies Rented column has multiple values. Now let's move into 1st Normal Forms:
The above table in 1NF-
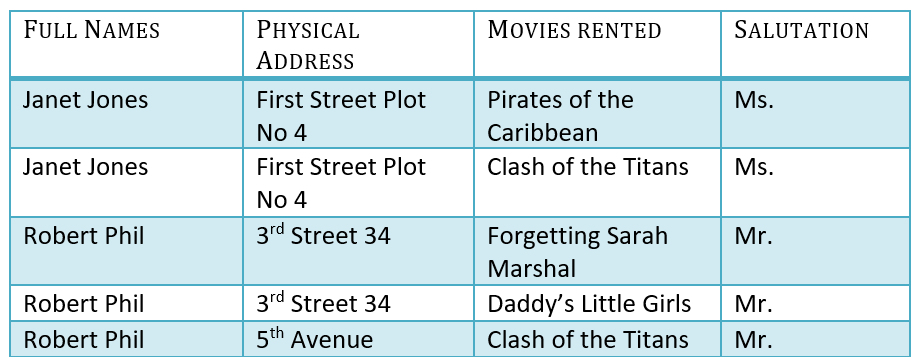
Before we proceed let's understand a few things --
A KEY is a value used to identify a record in a table uniquely. A KEY could be a single column or combination of multiple columns
Note: Columns in a table that are NOT used to identify a record uniquely are called non-key columns.

A primary is a single column value used to identify a database record uniquely.
It has following attributes
A composite key is a primary key composed of multiple columns used to identify a record uniquely
In our database, we have two people with the same name Robert Phil, but they live in different places.
Hence, we require both Full Name and Address to identify a record uniquely. That is a composite key.
Let's move into second normal form 2NF
It is clear that we can't move forward to make our simple database in 2nd Normalization form unless we partition the table above.
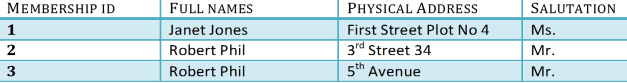 We have divided our 1NF table into two tables viz. Table 1 and Table2. Table 1 contains member information. Table 2 contains information on movies rented.
We have divided our 1NF table into two tables viz. Table 1 and Table2. Table 1 contains member information. Table 2 contains information on movies rented.
We have introduced a new column called Membership_id which is the primary key for table 1. Records can be uniquely identified in Table 1 using membership id
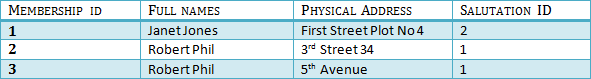
In Table 2, Membership_ID is the Foreign Key Foreign Key references the primary key of another Table! It helps connect your Tables
The above problem can be overcome by declaring membership id from Table2 as foreign key of membership id from Table1
Now, if somebody tries to insert a value in the membership id field that does not exist in the parent table, an error will be shown!
A transitive functional dependency is when changing a non-key column, might cause any of the other non-key columns to change
Consider the table 1. Changing the non-key column Full Name may change Salutation. Let's move into 3NF
To move our 2NF table into 3NF, we again need to again divide our table.
Below is a 3NF example in SQL database:
 Now our little example is at a level that cannot further be decomposed to attain higher normal forms of normalization. In fact, it is already in higher normalization forms. Separate efforts for moving into next levels of normalizing data are normally needed in complex databases. However, we will be discussing next levels of normalizations in brief in the following.
Now our little example is at a level that cannot further be decomposed to attain higher normal forms of normalization. In fact, it is already in higher normalization forms. Separate efforts for moving into next levels of normalizing data are normally needed in complex databases. However, we will be discussing next levels of normalizations in brief in the following.
Even when a database is in 3rd Normal Form, still there would be anomalies resulted if it has more than one Candidate Key.
Sometimes is BCNF is also referred as 3.5 Normal Form.
If no database table instance contains two or more, independent and multivalued data describing the relevant entity, then it is in 4th Normal Form.
A table is in 5th Normal Form only if it is in 4NF and it cannot be decomposed into any number of smaller tables without loss of data.
6th Normal Form is not standardized, yet however, it is being discussed by database experts for some time. Hopefully, we would have a clear & standardized definition for 6th Normal Form in the near future...
That's all to SQL Normalization!!!
$20.20 $9.99 for today 4.5 (108 ratings) Key Highlights of PL/SQL Tutorial PDF 188+ pages eBook...
In this SQL Query cheat sheet you will learn {loadposition table-of-content} What You Will Learn:...
In this tutorial, we will introduce SQL* Plus and learn how to connect it to the database. After...
Now that Myflixdb, what's next? Congratulations for your success completion of the SQL tutorial...
In this article, we will see how to create tables, modify tables and dropping tables in SQLite3...
What is Database Design? Database Design is a collection of processes that facilitate the...