SQL
MySQL Index Tutorial - Create, Add & Drop
What is an Index? Indexes in MySQL sort data in an organized sequential way. They are created on...
Data Independence is defined as a property of DBMS that helps you to change the Database schema at one level of a database system without requiring to change the schema at the next higher level. Data independence helps you to keep data separated from all programs that make use of it.
You can use this stored data for computing and presentation. In many systems, data independence is an essential function for components of the system.
In this tutorial, you will learn:
In DBMS there are two types of data independence
Before we learn Data Independence, a refresher on Database Levels is important. The database has 3 levels as shown in the diagram below
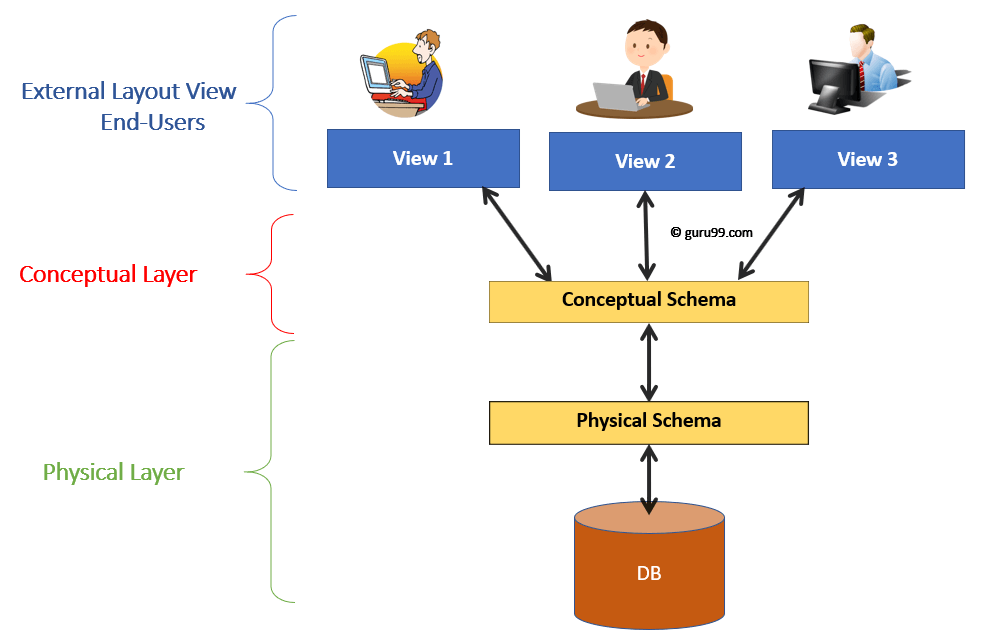
Consider an Example of a University Database. At the different levels this is how the implementation will look like:
| Type of Schema | Implementation |
| External Schema | View 1: Course info(cid:int,cname:string) View 2: studeninfo(id:int. name:string) |
| Conceptual Shema | Students(id: int, name: string, login: string, age: integer) Courses(id: int, cname.string, credits:integer) Enrolled(id: int, grade:string) |
| Physical Schema |
|
Physical data independence helps you to separate conceptual levels from the internal/physical levels. It allows you to provide a logical description of the database without the need to specify physical structures. Compared to Logical Independence, it is easy to achieve physical data independence.
With Physical independence, you can easily change the physical storage structures or devices with an effect on the conceptual schema. Any change done would be absorbed by the mapping between the conceptual and internal levels. Physical data independence is achieved by the presence of the internal level of the database and then the transformation from the conceptual level of the database to the internal level.
Due to Physical independence, any of the below change will not affect the conceptual layer.
Logical Data Independence is the ability to change the conceptual scheme without changing
Any change made will be absorbed by the mapping between external and conceptual levels.
When compared to Physical Data independence, it is challenging to achieve logical data independence.
Due to Logical independence, any of the below change will not affect the external layer.
| Logica Data Independence | Physical Data Independence |
| Logical Data Independence is mainly concerned with the structure or changing the data definition. | Mainly concerned with the storage of the data. |
| It is difficult as the retrieving of data is mainly dependent on the logical structure of data. | It is easy to retrieve. |
| Compared to Logic Physical independence it is difficult to achieve logical data independence. | Compared to Logical Independence it is easy to achieve physical data independence. |
| You need to make changes in the Application program if new fields are added or deleted from the database. | A change in the physical level usually does not need change at the Application program level. |
| Modification at the logical levels is significant whenever the logical structures of the database are changed. | Modifications made at the internal levels may or may not be needed to improve the performance of the structure. |
| Concerned with conceptual schema | Concerned with internal schema |
| Example: Add/Modify/Delete a new attribute | Example: change in compression techniques, hashing algorithms, storage devices, etc |
What is an Index? Indexes in MySQL sort data in an organized sequential way. They are created on...
In the daily use of SQLite, you will need some administrative tools over your database. You can...
Now that Myflixdb, what's next? Congratulations for your success completion of the SQL tutorial...
In this tutorial, you will learn- SQLite constraint Primary Key Not null constraint DEFAULT...
What is MySQL 5.6 Certification? The new release of MySQL 5.6 is designed for professionals...
In SQL Null is both a value as well as a keyword. Let's look into NULL value first - Null as a...