SDLC
SSD Vs HDD: What's the Difference? | Which one to Choose?
In this article of SSD vs HDD differences, we will learn the key SSD and HDD difference. But...
Deadlock is a situation that occurs in OS when any process enters a waiting state because another waiting process is holding the demanded resource. Deadlock is a common problem in multi-processing where several processes share a specific type of mutually exclusive resource known as a soft lock or software.
In this operating system tutorial, you will learn:
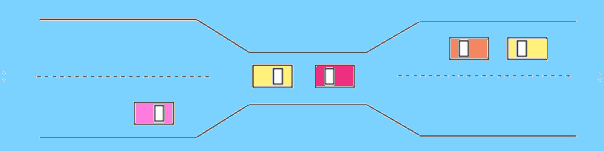
One process is waiting for the resource, which is held by the second process, which is also waiting for the resource held by the third process etc. This will continue until the last process is waiting for a resource held by the first process. This creates a circular chain.
For example, Process A is allocated Resource B as it is requesting Resource A. In the same way, Process B is allocated Resource A, and it is requesting Resource B. This creates a circular wait loop.
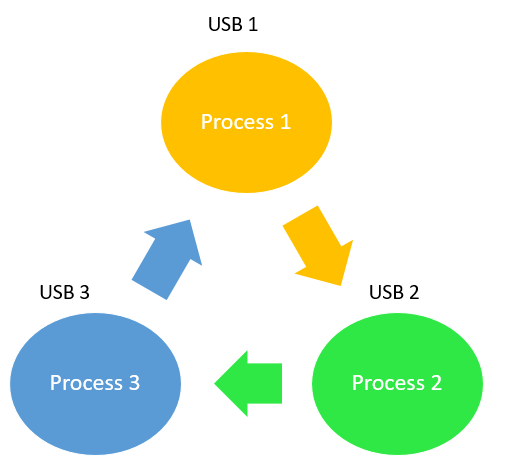
For example, a computer has three USB drives and three processes. Each of the three processes able to holds one of the USB drives. So, when each process requests another drive, the three processes will have the deadlock situation as each process will be waiting for the USB drive to release, which is currently in use. This will result in a circular chain.
A deadlock occurrence can be detected by the resource scheduler. A resource scheduler helps OS to keep track of all the resources which are allocated to different processes. So, when a deadlock is detected, it can be resolved using the below-given methods:
It's important to prevent a deadlock before it can occur. The system checks every transaction before it is executed to make sure it doesn't lead the deadlock situations. Such that even a small change to occur dead that an operation which can lead to Deadlock in the future it also never allowed process to execute.
It is a set of methods for ensuring that at least one of the conditions cannot hold.
No Preemption - A resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it after that process has finished its task
Mutual Exclusion is a full form of Mutex. It is a special type of binary semaphore which used for controlling access to the shared resource. It includes a priority inheritance mechanism to avoid extended priority inversion problems. It allows current higher priority tasks to be kept in the blocked state for the shortest time possible.
Resources shared such as read-only files never lead to deadlocks, but resources, like printers and tape drives, needs exclusive access by a single process.
In this condition, processes must be stopped from holding single or multiple resources while simultaneously waiting for one or more others.
It imposes a total ordering of all resource types. Circular wait also requires that every process request resources in increasing order of enumeration.
It is better to avoid a deadlock instead of taking action after the Deadlock has occurred. It needs additional information, like how resources should be used. Deadlock avoidance is the simplest and most useful model that each process declares the maximum number of resources of each type that it may need.
The deadlock-avoidance algorithm helps you to dynamically assess the resource-allocation state so that there can never be a circular-wait situation.
A single instance of a resource type.
Multiples instances of a resource type.
Here, are some important differences between Deadlock and starvation:
| Deadlock | Starvation |
| The deadlock situation occurs when one of the processes got blocked. | Starvation is a situation where all the low priority processes got blocked, and the high priority processes execute. |
| Deadlock is an infinite process. | Starvation is a long waiting but not an infinite process. |
| Every Deadlock always has starvation. | Every starvation does n't necessarily have a deadlock. |
| Deadlock happens then Mutual exclusion, hold and wait. Here, preemption and circular wait do not occur simultaneously. | It happens due to uncontrolled priority and resource management. |
Here, are pros/benefits of using Deadlock method
Here, are cons/ drawback of using deadlock method
In this article of SSD vs HDD differences, we will learn the key SSD and HDD difference. But...
Wireless Keyboard and Mouse enables you to eliminate wires to make your workstation clean and...
In this tutorial, we will take you through step by step process to install Apache Hadoop on a...
IP camera software are applications that can be used for home surveillance, business, and family...
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} Remote administration tools help IT professionals to debug...
PC optimization improves the life of your PC, and prevents the virus, bugs, malware from infecting your...