Ethical Hacking
6 Best VPN for China | Tested & Working in Feb 2021 (FREE)
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} China has placed numerous restrictions on...
Circuit switching was designed in 1878 to send telephone calls down a dedicated channel. It is a method that is used when a dedicated channel or circuit needs to be established.
A channel used in circuit switching is kept reserved and applied only when the two users need to communicate.
Circuit switching connections are classified into two categories half-duplex or full-duplex. Half-duplex communications can be allocated just one channel, while full-duplex interfaces can be assigned two channels.
Packet switching is a method of grouping data that is transmitted over a digital network into packets. It is a connectionless network switching method. It never establishes any physical connection before the transmission starts. In the packet switching method, before the message is transmitted, it is divided into some manageable parts known as packets.
In this method, each packet divided into two parts: a header and a payload. The header contains the addressing information of the packet. The payload contains the actual message.
| Item | Circuit-switched | Packet-switched |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth available | Fixed | No |
| Dedicated "copper" path | Yes | Dynamic |
| When can congestion occur | At setup time | On every packet |
| Possibly wasted bandwidth | Yes | Yes |
| Store-and-forward transmission | No | No |
| Each packet follows the same route | Yes | Not necessary |
| Call setup | Required | Not required |
| Charging | Per minute | Per packet |
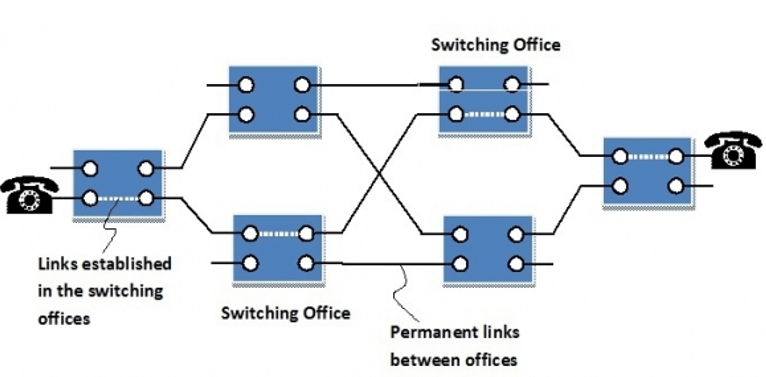
The given diagram shows how the circuit established between two telephones connected by circuit switch connection. The boxes represent the switching offices and their connection with another telephone office. The blue line represents a connection between both the offices.
Whenever a connection is requested, the links can be established within the switching office, denoted by circles. It has a dedicated circuit established between the communication parties. These links remain as long as communication remains.
All the packets are sent with a 'header address' which tells it where its final destination is, so it knows where to go.
The header address also illustrates the sequence for reassembly at the destination computer so that the packets are rearrange into the correct order.
In this method, one packet also contains details of how many packets should be arriving so that the recipient computer knows if any packet has failed to turn up.
In case if a packet fails to arrive, the recipient computer sends a message back to the sender's computer, asking for the missing packet to be resent.
Here are the main differences between Circuit Switching and Packet Switching:
| Circuit – Switching | Packet – Switching |
|---|---|
| Circuit switching is a method that is used when a dedicated channel or circuit needs to be established. | Packet switching is a method of grouping data which is transmitted over a digital network into packets. |
| Circuit switching connections are classified into two categories half-duplex or full-duplex. | Packet Switching is a connectionless network switching method. |
| You need to establish a dedicated path between the source and the destination before the transfer of data commences. | You do not need to establish a dedicated path from the source to the destination. |
| It was initially designed for voice transfer. | It was initially designed for data transfer. |
| It is implemented at Physical Layer. | It is implemented at Network Layer. |
| In-Circuit switching, data is processed and transmitted at the source only. | In packet switching, data is processed and transmitted, not only at the source but also at the destination. |
| Its initial cost is low. | Packet switching demands high installation costs. |
| The protocols for delivery are simpler. | It requires complex protocols for delivery. |
| Charging happens per minute. | Charging happens per packet. |
| Each packet follows the same route. | Each packet does not follow the same route. |
| It does not store and forward transmission. | It does store and forward transmission. |
| Initially designed for Voice communication. | Initially designed for Data Transmission. |
| It is an inflexible method because once a path is set, all parts of a transmission follow the same path. | It is a flexible method because the route is created for each packet to travel to the destination. |
| The message is received in the order, which is sent from the source. | In, packet switching message are received out of order, which is assembled at the destination. |
| Reserve the entire Bandwidth in advance. | Never reserves the Bandwidth. |
| You can achieve Circuit switching using two technologies 1) Time or 2) Space Division Switching. | Packet Switching has Datagram Virtual Circuit Approach. |
Here, are pros/benefits of Circuit Switching:
Here, are pros/benefits of Packet Switching method:
Here, are some cons/drawbacks of circuit switching method:
Here, are some cons/drawbacks of Packet Switching method:
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} China has placed numerous restrictions on...
Some of the skills that hackers have are programming and computer networking skills. They often...
More people have access to the internet than ever before. This has prompted many organizations to...
Computers communicate using networks. These networks could be on a local area network LAN or...
Cybersecurity refers to protecting hardware, software, and data from attackers. It protects...
Data is one of the most vital components of information systems. Database powered web applications are used by...