Cucumber
How to Download & Install CUCUMBER in Windows
Cucumber installation could be tiresome but its relatively easy. Here is a roadmap of components that need...
Gherkin is a business readable language which helps you to describe business behavior without going into details of implementation. It is a domain specific language for defining tests in Cucumber format for specifications. It uses plain language to describe use cases and allows users to remove logic details from behavior tests.
The text in Gherkin langauge acts as documentation and skeleton of your automated tests. Gherkin format is based on TreeTop Grammar which exists in 37+ languages. Therefore you can write your gherkin in 37+ spoken languages.
This script serves two primary purposes:
In this Gherkin tutorial, you will learn
The need for Gherkin can be easily explained by following images
Before Gherkin
After Gherkin
Gherkin is line-oriented language just like YAML and Python. Each line called step and starts with keyword and end of the terminals with a stop. Tab or space are used for the indentation.
In this script, a comment can be added anywhere you want, but it should start with a # sign. It read each line after removing Ghrekin's keywords as given, when, then, etc.
Gherkin Scripts: connects the human concept of cause and effect to the software concept of input/process/output.
Feature: Title of the Scenario Given [Preconditions or Initial Context] When [Event or Trigger] Then [Expected output]
A Gherkin document has an extension .feature and simply just a test file with a fancy extension. Cucumber reads Gherkin document and executes a test to validate that the software behaves as per the Gherkin syntax.
The naming convention is used for feature name. However, there is no set rules in Cucumber about names.
The file should have extension .feature and each feature file should have only one feature. The feature keyword being with the Feature: and after that add, a space and name of the feature will be written.
Each feature file may have multiple scenarios, and each scenario starts with Scenario: followed by scenario name.
Background keyword helps you to add some context to the scenario. It can contain some steps of the scenario, but the only difference is that it should be run before each scenario.
The use of Given keyword is to put the system in a familiar state before the user starts interacting with the system. However, you can omit writing user interactions in Given steps if Given in the "Precondition" step.
Syntax:
Given
Given - a test step that defines the 'context Given I am on "/."
When the step is to define action performed by the user.
Syntax:
When
A When - a test step that defines the 'action' performed When I perform "Sign In."
The use of 'then' keyword is to see the outcome after the action in when step. However, you can only verify noticeable changes.
Syntax:
Then
Then - test step that defines the 'outcome.' Then I should see "Welcome Tom."
You may have multiple given when or Then.
Syntax:
But
A But - additional test step which defines the 'action' 'outcome.' But I should see "Welcome Tom."
And - additional test step that defines the 'action' performed
And I write "EmailAddress" with "This email address is being protected from spambots. You need JavaScript enabled to view it.."Given, When, Then, and, but are test steps. You can use them interchangeably. The interpreter doesn't display any error. However, they will surely not make any 'sense' when read.
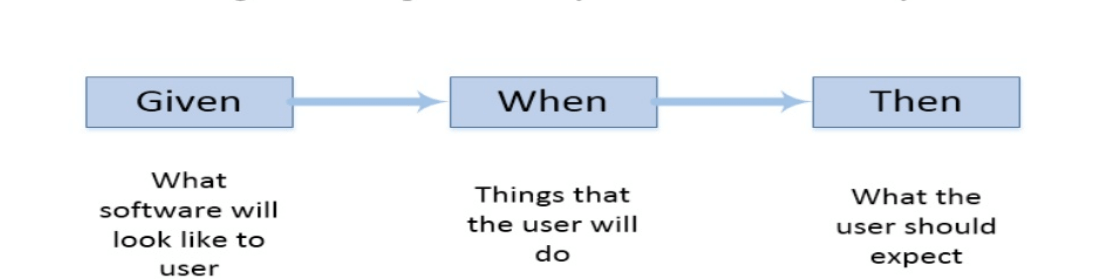
Important Terms used in Gherkin
Given The login page is opening When I input username, password and click the Login button Then I am on the Homepage
Example 1:
Feature: Login functionality of social networking site Facebook. Given: I am a facebook user. When: I enter username as username. And I enter the password as the password Then I should be redirected to the home page of facebook
The scenario mentioned above is of a feature called user login.
All the words written in bold are Gherkin keywords.
Gherkin will analyze each step written in the step definition file. Therefore, the steps are given in the feature file and the step definition file should match.
Example 2:
Feature: User Authentication Background: Given the user is already registered to the website Scenario: Given the user is on the login page When the user inputs the correct email address And the user inputs the correct password And the user clicks the Login button Then the user should be authenticated And the user should be redirected to their dashboard And the user should be presented with a success message
Cucumber installation could be tiresome but its relatively easy. Here is a roadmap of components that need...
For every cucumber project there is a single directory at the root of the project named " features...
What is Cucumber? Cucumber is a testing tool that supports Behavior Driven Development (BDD). It...
Training Summary Behavior Driven Development (BDD) is a rising methodology to test and check your...
In this tutorial, we will create Cucumber Scripts to test two scenarios Cucumber Script 1:...