Ethical Hacking
How to Crack a Password
What is Password Cracking? Password cracking is the process of attempting to gain Unauthorized...
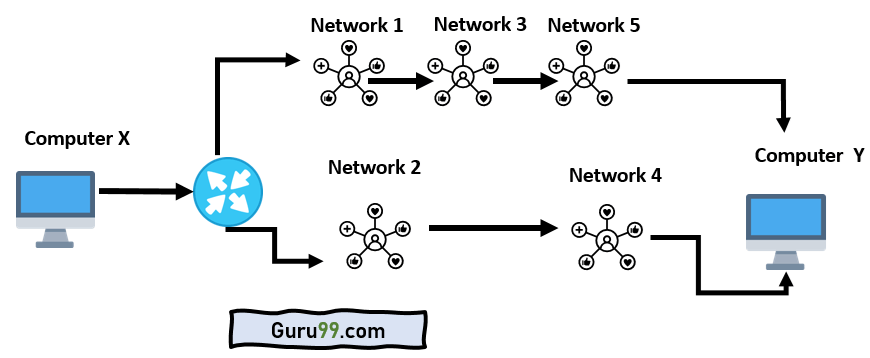
IP Routing is a process that sends packets from a host on one network to another host on a different remote network. It helps you examine the destination IP address of a packet, determine the next-hop address, and forward it. IP routers use routing tables to determine the next-hop address to which the packet should be delivered.
In CISCO IP routing, data is routed from its source to its destination through routers and across multiple networks. The IP Routing protocols allow routers to build up a forwarding table that correlates final destinations with next-hop addresses.
In this networking tutorial, you will learn:
Routing metric are the value that allows the routers to decide the best route for the data packet
Different routing metrics are:
Consider the below given image-
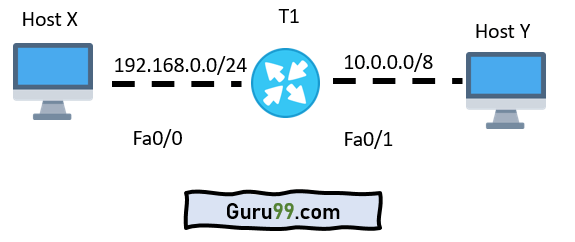
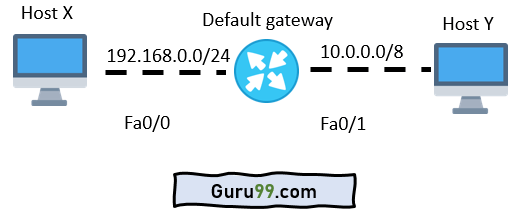
A default gateway is a router that hosts use to communicate with other hosts on remote networks. A default gateway is used when a host does not have a route entry for the particular remote network and does not know how to reach that network.
Hosts should be configured to send all packets destined to the default gateway's remote networks, which has a route to reach that specific network.
The following example explains the concept of a default gateway more thoroughly.
Every router maintains a routing table which is stored in its RAM. A routing table is widely used by routers to decide the path to the destination network. There are mainly three different methods for populating a routing table:
The following protocols help data packets find their way across the Internet:
The Internet Protocol (IP) specifies the origin and destination for each data packet. Routers inspect each packet's IP header to identify where to send them.
RIP is used in both LAN and WAN Networks. It also runs on the application layer of the OSI model. The full form of RIP is the Routing Information Protocol. Two versions of RIP are
It is a hybrid routing protocol that provides routing protocols, distance vector, and link-state routing protocols. It will route the same protocols that IGRP routes using the same composite metrics as IGRP, which helps the network select the best path destination.
ISIS routing protocol is used on the Internet to send IP routing information. It consists of a range of components, including end systems, intermediate systems, areas, and domains.
BGP is a routing protocol of the Internet, which is classified as a DPVP (distance path vector protocol). The full form of BGP is the Border Gateway Protocol.
The routing process ensures that appropriate packets are routed from the source to the destination
Goals of routing include:
Routers are computer networking devices that serve two primary functions:
It also helps you to handle multiple networks and routes network traffic between them. In your home network, your router has one connection to the Internet and one connection to your private local network. Moreover, most routers also contain built-in switches that allow you to connect multiple wired devices.
Here are important functions of Router:
What is Password Cracking? Password cracking is the process of attempting to gain Unauthorized...
Data is one of the most vital components of information systems. Database powered web applications are used by...
Ethical hacking is identifying weaknesses in computer systems or networks to exploit its...
Anti-spyware removes malicious spyware and protects your computer system. They detect and remove...
Customers usually turn to the internet to get information and buy products and services. Towards...
YouTube TV is one of the most famous streaming services. VPN or Virtual Private Network helps you...