Java Tutorials
Java Swing Tutorial: How to Create a GUI in Java with Examples
What is Swing in Java? Swing in Java is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) toolkit that includes the GUI...
Abstraction in JAVA shows only the essential attributes and hides unnecessary details of the object from the user. In Java, abstraction is accomplished using Abstract class, Abstract methods, and Interfaces. Abstraction helps in reducing programming complexity and effort.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
ABSTRACT CLASS is a type of class in Java, that declare one or more abstract methods. These classes can have abstract methods as well as concrete methods. A normal class cannot have abstract methods. An abstract class is a class that contains at least one abstract method. We can understand the concept by the shape example in java.
Consider the following class hierarchy consisting of a Shape class which is inherited by three classes Rectangle, Circle, and Triangle. The Shape class is created to save on common attributes and methods shared by the three classes Rectangle, Circle, and Triangle. calculateArea() is one such method shared by all three child classes and present in Shape class.
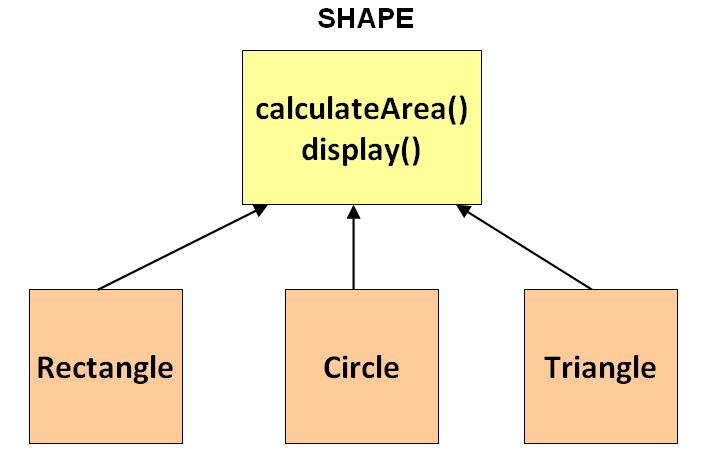
Now, assume you write code to create objects for the classes depicted above. Let's observe how these objects will look in a practical world.
An object of the class rectangle will give a rectangle, a shape we so commonly observed in everyday life.
An object of the class triangle will give a triangle, again a common everyday shape.
But what would an object of Class Shape look like in a practical world ??
If you observe the Shape class serves in our goal of achieving inheritance and polymorphism. But it was not built to be instantiated. Such classes can be labelled Abstract. An abstract java class cannot be instantiated.
Syntax:
abstract class Shape{
// code
}
It is possible that you DO NOT label Shape class as Abstract and then instantiate it. But such object will have no use in your code and will open a room for potential errors. Hence this is not desirable.
ABSTRACT METHOD in Java, is a method that has just the method definition but does not contain implementation. A method without a body is known as an Abstract Method. It must be declared in an abstract class. The abstract method will never be final because the abstract class must implement all the abstract methods.
As we all know, the formula for calculating area for rectangle, circle, & triangle is different. The calculateArea() method will have to be overridden by the inheriting classes. It makes no sense defining it in the Shape class, but we need to make sure that all the inheriting classes do have the method.
Such methods can be labeled abstract.
Syntax:
abstract public void calculateArea();
For an abstract method, no implementation is required. Only the signature of the method is defined.
abstract class Shape{
abstract void calculateArea();
}
public class gtupapers extends Shape{
void calculateArea(){System.out.println("Area of Shape");}
public static void main(String args[]){
Shape obj = new gtupapers();
obj.run();
}
}
The final modifier applies to classes, methods, and variables. The meaning of final varies from context to context, but the essential idea is the same.
Example :- To learn abstract & final keywords
Step 1) Copy the following code into an Editor.
abstract class Shape{
final int b = 20;
public void display(){
System.out.println("This is display method");
}
abstract public void calculateArea();
}
public class Rectangle extends Shape{
public static void main(String args[]){
Rectangle obj = new Rectangle();
obj.display();
//obj.b=200;
}
//public void calculateArea(){}
}
Step 2) Save , Compile & Run the code.
Step 3) Error =? The abstract method is not implemented int the class Rectangle. To fix the issue uncomment line #15.
Step 4) Uncomment line # 13 . Save & Compile the code.
Step 5) Error = ? variable b is final
Rules of Abstract Method
What is Swing in Java? Swing in Java is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) toolkit that includes the GUI...
What is a Variable in Java? Variable in Java is a data container that stores the data values...
What is Java? Java was released by Sun Microsystem in 1995. It was developed by James Gosling. It is a...
What is Java? Java is a multi-platform, object-oriented, and network-centric, programming...
1. tolowercase() method This Java string method converts every character of the particular string...
In this tutorial, we will study programs to To convert a character to String To convert a String to...