Java Tutorials
Java String contains() Method | Check Substring with Example
Java String contains() method The Java String contains() method is used to check whether the...
Inheritance is a mechanism in which one class acquires the property of another class. For example, a child inherits the traits of his/her parents. With inheritance, we can reuse the fields and methods of the existing class. Hence, inheritance facilitates Reusability and is an important concept of OOPs.
In this tutorial, you will learn-
There are Various types of inheritance in Java:
In Single Inheritance one class extends another class (one class only).
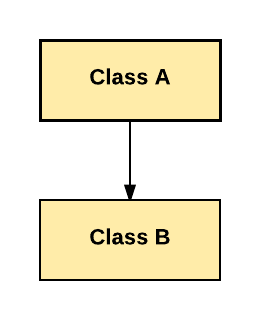
In above diagram, Class B extends only Class A. Class A is a super class and Class B is a Sub-class.
In Multiple Inheritance, one class extending more than one class. Java does not support multiple inheritance.
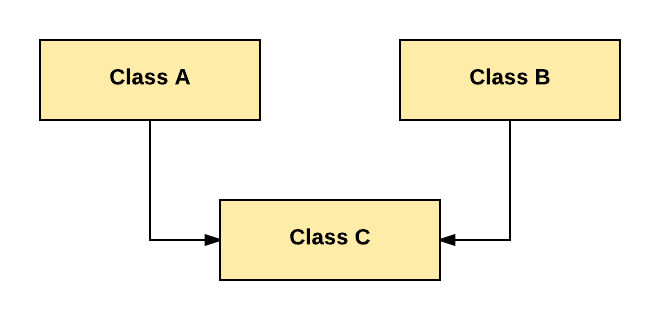
As per above diagram, Class C extends Class A and Class B both.
In Multilevel Inheritance, one class can inherit from a derived class. Hence, the derived class becomes the base class for the new class.
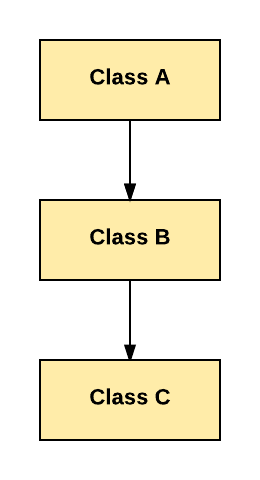
As per shown in diagram Class C is subclass of B and B is a of subclass Class A.
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class is inherited by many sub classes.
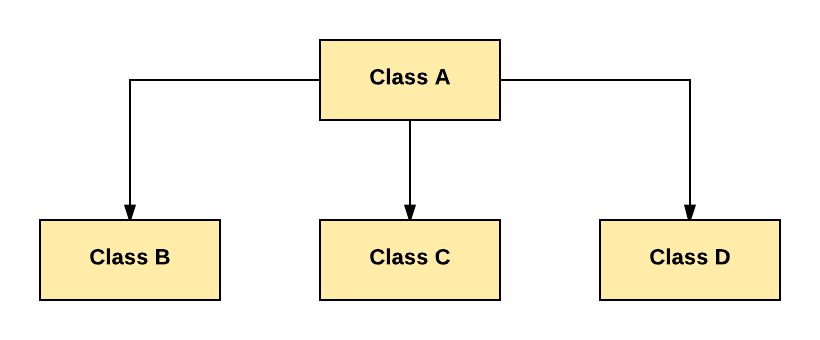
As per above example, Class B, C, and D inherit the same class A.
Hybrid inheritance is a combination of Single and Multiple inheritance.
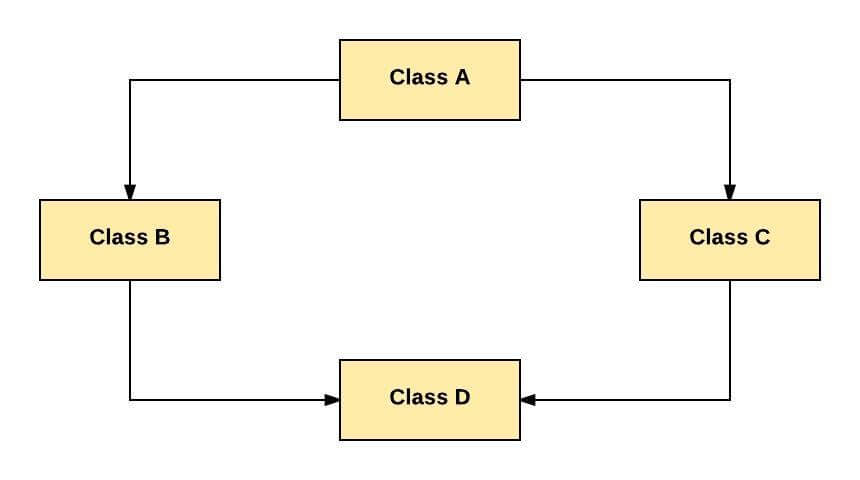
As per above example, all the public and protected members of Class A are inherited into Class D, first via Class B and secondly via Class C.
Note: Java doesn't support hybrid/Multiple inheritence
JAVA INHERITANCE is a mechanism in which one class acquires the property of another class. In Java, when an "Is-A" relationship exists between two classes, we use Inheritance. The parent class is called a super class and the inherited class is called a subclass. The keyword extends is used by the sub class to inherit the features of super class.
Inheritance is important since it leads to the reusability of code.
Java Inheritance Syntax:
class subClass extends superClass
{
//methods and fields
}
The keyword super can be used to access any data member or methods of the parent class.
Super keyword can be used at variable, method and constructor level.
Syntax:
super.<method-name>();
Consider the same banking application from the previous example.
We are supposed to open two different account types, one for saving and another for checking (also known as current).
The functions are not required to be implemented individually. This is Inheritance in java. .
Java String contains() method The Java String contains() method is used to check whether the...
You can use JavaScript code in two ways. You can either include the JavaScript code internally within...
What is Function in JavaScript? Functions are very important and useful in any programming language...
What is Interface? The interface is a blueprint that can be used to implement a class. The...
Follow the simple steps below to compile and execute any JAVA program online using your favourite...
Any application can have multiple processes (instances). Each of this process can be assigned...