JavaScript
What is JavaScript? Complete Introduction with Hello World! Example
In this tutorial, you will learn- What is JavaScript? Javascript History How to Run JavaScript? Tools...
Swing in Java is a Graphical User Interface (GUI) toolkit that includes the GUI components. Swing provides a rich set of widgets and packages to make sophisticated GUI components for Java applications. Swing is a part of Java Foundation Classes(JFC), which is an API for Java programs that provide GUI.
The Java Swing library is built on top of the Java Abstract Widget Toolkit (AWT), an older, platform dependent GUI toolkit. You can use the Java GUI programming components like button, textbox, etc. from the library and do not have to create the components from scratch.
In this Java Swing tutorial, you will learn-
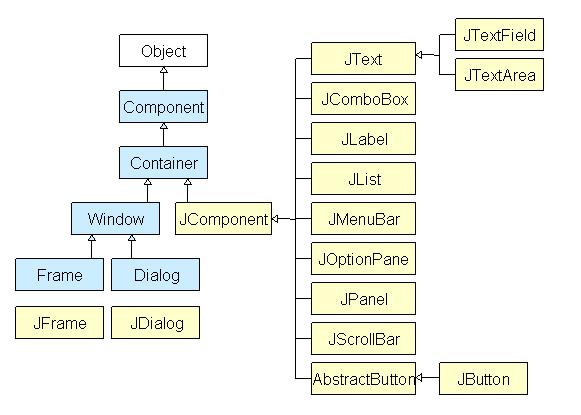
All components in Java Swing are JComponent which can be added to container classes.
Container classes are classes that can have other components on it. So for creating a Java GUI, we need at least one container object. There are 3 types of Java Swing containers.
GUI (Graphical User Interface) in Java is an easy-to-use visual experience builder for Java applications. It is mainly made of graphical components like buttons, labels, windows, etc. through which the user can interact with an application. GUI plays an important role to build easy interfaces for Java applications.
Now in this Swing Java Tutorial, let's understand GUI with Java Swing examples.
Example: To learn Java GUI programming in this Java GUI tutorial
Step 1) Copy the following code into an editor
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button = new JButton("Press");
frame.getContentPane().add(button); // Adds Button to content pane of frame
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 2) Save, Compile, and Run the code.
Step 3) Now let's Add a Button to our frame. Copy following code into an editor from given Java GUI Example
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button1 = new JButton("Press");
frame.getContentPane().add(button1);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 4) Execute the code. You will get a big button Step 5) How about adding two buttons? Copy the following code into an editor.
import javax.swing.*;
class gui{
public static void main(String args[]){
JFrame frame = new JFrame("My First GUI");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setSize(300,300);
JButton button1 = new JButton("Button 1");
JButton button2 = new JButton("Button 2");
frame.getContentPane().add(button1);
frame.getContentPane().add(button2);
frame.setVisible(true);
}
}
Step 6) Save , Compile , and Run the program.
Step 7) Unexpected output =? Buttons are getting overlapped.
The Layout manager is used to layout (or arrange) the GUI java components inside a container.There are many layout managers, but the most frequently used are-
BorderLayout places components in up to five areas: top, bottom, left, right, and center. It is the default layout manager for every java JFrame FlowLayout is the default layout manager for every JPanel. It simply lays out components in a single row one after the other. It is the more sophisticated of all layouts. It aligns components by placing them within a grid of cells, allowing components to span more than one cell. Step 8) How about creating a chat frame like below?
In this tutorial, you will learn- What is JavaScript? Javascript History How to Run JavaScript? Tools...
JavaScript is the most popular client-side scripting language supported by all browsers. It is...
Any application can have multiple processes (instances). Each of this process can be assigned...
What is Stack Memory? Stack in java is a section of memory which contains methods, local...
What is ArrayList in Java? ArrayList in Java is a data structure that can be stretched to...
Java throws keyword The Java throws keyword is used to declare the exception information that may occur...