Linux
20 Best FTP Client for Windows & Mac [Free/Paid]
FTP clients are software designed specifically to transfer files between PC and servers over...
Before we start this Kubernetes tutorial, let's learn:
Today's internet user never accept downtime. Therefore developers have to find a method to perform maintenance and update without interrupting their services.
Therefore container, which is isolated environments. It includes everything needed for application to run. It makes it easy for a developer to edit and deploying apps. Moreover, containerization has become a preferred method for packaging, deploying, and update web apps.
Kubernetes is a container management system developed on the Google platform. Kubernetes helps to manage containerised applications in various types of physical, virtual, and cloud environments. Google Kubernetes is a highly flexible container tool to consistently deliver complex applications running on clusters of hundreds to thousands of individual servers.
In this Kubernetes tutorial for beginners, you will learn Kubernetes basics like:
Kubernetes is the Linux kernel which is used for distributed systems. It helps you to be abstract the underlying hardware of the nodes(servers) and offers a consistent interface for applications that consume the shared pool of resources.
Kubernetes helps you to control the resource allocation and traffic management for cloud applications and microservices. It also helps to simplify various aspects of service-oriented infrastructures. Kubernetes allows you to assure where and when containerized applications run and helps you to find resources and tools you want to work with.
Here are the essential Kubernetes features:
Now in this Kubernetes tutorial, we will learn some important Basics of Kubernetes:
Below is a detailed Kubernetes architecture diagram: 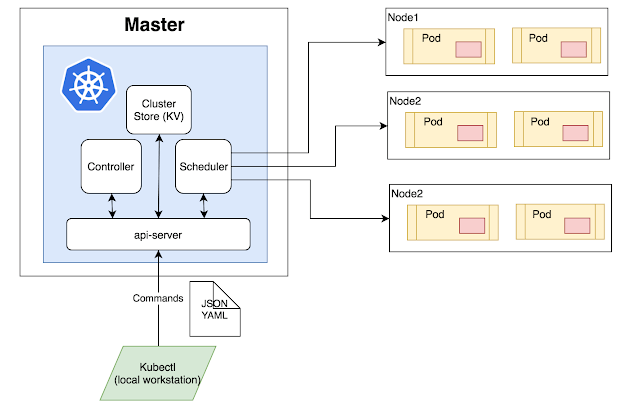
The master node is the first and most vital component which is responsible for the management of Kubernetes cluster. It is the entry point for all kind of administrative tasks. There might be more than one master node in the cluster to check for fault tolerance.
The master node has various components like API Server, Controller Manager, Scheduler, and ETCD. Let see all of them.
API Server: The API server acts as an entry point for all the REST commands used for controlling the cluster.
The scheduler schedules the tasks to the slave node. It stores the resource usage information for every slave node. It is responsible for distributing the workload.
It also helps you to track how the working load is used on cluster nodes. It helps you to place the workload on resources which are available and accept the workload.
etcd components store configuration detail and wright values. It communicates with the most component to receive commands and work. It also manages network rules and port forwarding activity.
Worker nodes are another essential component which contains all the required services to manage the networking between the containers, communicate with the master node, which allows you to assign resources to the scheduled containers.
A replication controller is an object which defines a pod template. It also controls parameters to scale identical replicas of Pod horizontally by increasing or decreasing the number of running copies.
Replication sets are an interaction on the replication controller design with flexibility in how the controller recognizes the pods it is meant to manage. It replaces replication controllers because of their higher replicate selection capability.
Deployment is a common workload which can be directly created and manage. Deployment use replication set as a building block which adds the feature of life cycle management.
It is a specialized pod control which offers ordering and uniqueness. It is mainly used to have fine-grained control, which you have a particular need regarding deployment order, stable networking, and persistent data.
Daemon sets are another specialized form of pod controller that runs a copy of a pod on every node in the cluster. This type of pod controller is an effective method for deploying pods that allows you to perform maintenance and offers services for the nodes themselves.
Here are important differences between Kubernetes vs Docker.
| Parameters | Docker Swarm | Kubernetes |
| Scaling | No Autoscaling | Auto-scaling |
| Load balancing | Does auto load balancing | Manually configure your load balancing settings |
| Storage volume sharing | Shares storage volumes with any other container | Shares storage volumes between multiple containers inside the same Pod |
| Use of logining and monitoring tool | Use 3rd party tool like ELK | Provide an in-built tool for logging and monitoring. |
| Installation | Easy & fast | Complicated & time-consuming |
| GUI | GUI not available | GUI is available |
| Scalability | Scaling up is faster than K8S, but cluster strength not as robust | Scaling up is slow compared to Swarm, but guarantees stronger cluster state Load balancing requires manual service configuration |
| Load Balancing | Provides a built-in load balancing technique | Process scheduling to maintain services while updating |
| Updates & Rollbacks Data Volumes Logging & Monitoring | Progressive updates and service health monitoring. | Only shared with containers in same Pod Inbuilt logging & monitoring tools. |
FTP clients are software designed specifically to transfer files between PC and servers over...
MAC includes a huge collection of the built-in app. However, there are many useful software that...
What is 32-Bit? 32-bit is a type of CPU architecture which is capable of transferring 32 bits of...
When people talk about the essentials for the perfect gaming experience, many of them forget to...
New Relic's is a leading tool for application performance monitoring (APM). It offers real-time...
What is CISC? CISC was developed to make compiler development easier and simpler. The full form of...