Linux
Top 60 Linux Interview Questions and Answers (Download PDF)
We have organized the most frequently asked Linux Interview Questions and Answers that help...
The MVC framework is an architectural pattern that separates an applications into three main logical components Model, View, and Controller. Hence the abbreviation MVC. The full form MVC is Model View Controller.
In this architecture, a component is built to handle specific development aspects of an application. MVC separates the business logic and presentation layer from each other. This architectural pattern mainly used for desktop graphical user interfaces (GUIs).
In this tutorial, you will learn:
MVVM architecture facilitates a separation of development of the graphical user interface with the help of mark-up language or GUI code. The full form of MVVM is Model–View–ViewModel.
The view model of MVVM is a value converter that means that it is view model's responsibility for exposing the data objects from the Model in such a way that objects are easily managed and presented.
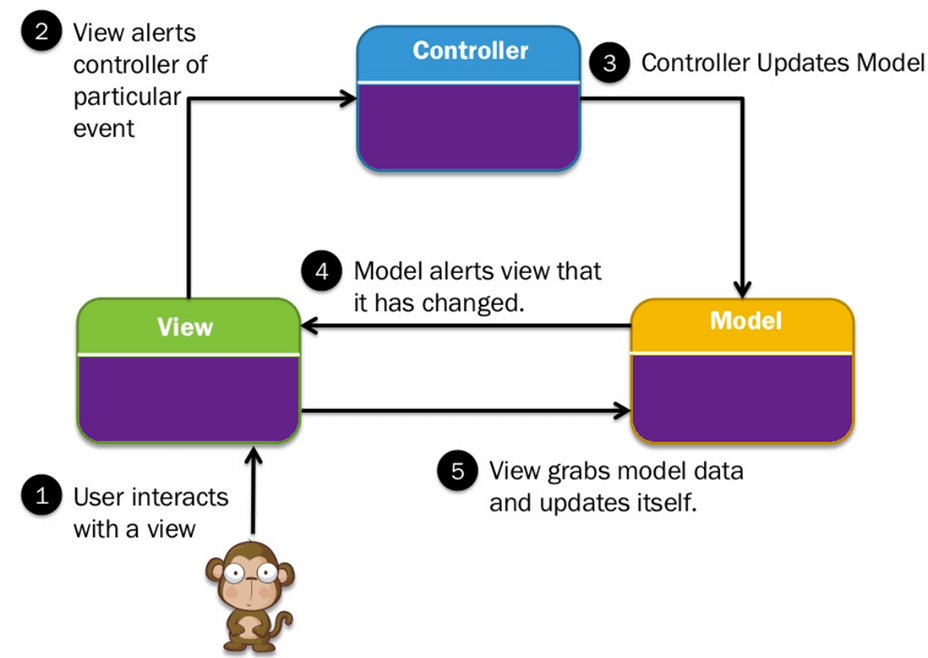
Three important MVC the components are:
Let's see each of this component in detail:
The model component stores data and related logic. It represents data that is being transferred between controller components or any other related business logic.
For example, a Controller object helps you to retrieve the customer info from the database. It manipulates data and sends it back to the database or use it to render the same data.
A View is that part of the Application that represents the presentation of data. Views are created by the data gathered from the model data. A view requests the Model to give information so that it resents the output to the user.
The View also represents the data from charts, diagrams, and table. For example, any customer view will include all the UI components like text boxes, dropdowns, etc.
The Controller is that part of the Application that handles the user interaction. The Controller interprets the mouse and keyboard inputs from the user, informing the Model and the View to change as appropriate.
A Controller sends commands to the Model to update its state(E.g., Saving a specific document). The Controller also sends commands to its associated view to change the View's presentation (For example, scrolling a particular document).
Here, is a pattern for MVVM:
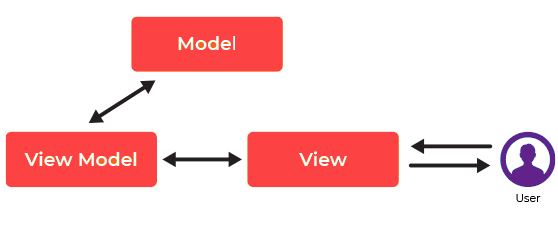
MVVM architecture offers two-way data binding between view and view-model. It also helps you to automate the propagation of modifications inside View-Model to the view. The view-model makes use of observer pattern to make changes in the view-model.
Let's see each other this component in detail:
The model stores data and related logic. It represents data that is being transferred between controller components or any other related business logic.
For example, a Controller object will retrieve the student info from the school database. It manipulates data and sends it back to the database or use it to render the same data.
The View stands for UI components like HTML, CSS, jQuery, etc. In MVVC pattern view is held responsible for displaying the data which is received from the Controller as an outcome. This View is also transformed Model (s) into the User Interface (UI).
The view model is responsible for presenting functions, commands, methods, to support the state of the View. It is also accountable to operate the model and activate the events in the View.
Here are important features of MVC:
Here, are features of MVVM architecture:
Here, are the important difference between MVVM and MVC
| MVC | MVVM |
| Controller is the entry point to the Application. | The view is the entry point to the Application. |
| One to many relationships between Controller & View. | One to many relationships between View & View Model. |
| View Does not have reference to the Controller | View have references to the View-Model. |
| MVC is Old Model | MVVM is a relatively New Model. |
| Difficult to read, change, to unit test, and reuse this Model | The debugging process will be complicated when we have complex data bindings. |
| MVC Model component can be tested separately from the user | Easy for separate unit testing and code is event-driven. |
Here, are advantages/pros of MVC
Here, are pros/benefits of MVVM
Here, are cons/drawback of MVC
Here, are cons/drawback of MVVM
We have organized the most frequently asked Linux Interview Questions and Answers that help...
What is a Program? A program is an executable file which contains a certain set of instructions written...
Front End Development Tool is a software application which helps developers to build attractive...
A bar chart is a great way to display categorical variables in the x-axis. This type of graph...
Now that we know what Linux is, it is the time that to learn how we should install it on the...
In this tutorial, you will learn- What is a Process? Running a Foreground Process Running a...