PL-SQL
Oracle PL/SQL Exception Handling: Examples to Raise User-defined Exception
What is Exception Handling in PL/SQL? An exception occurs when the PL/SQL engine encounters an...
Again, in real life, we perform different actions depending upon the outcome of different conditions.
To elaborate more, consider below example:
Let's consider categorizing Condition and Action separately from the above example below:
| Conditions – Flight Tickets | Actions performed, only if Condition is TRUE |
| Less than $100 | Visit Los Angeles |
| Between $100 to $200 | Visit New York |
| Between $200 to $400 | Visit Europe |
| None of the above condition met | Nearby tourist spot |
In the above example, we can see that the outcome of the different conditions is governing separate action. E.g., Visitor will perform the act of visiting New York only in the condition if the flight ticket is between $100 to $200.
Similarly, MS SQL CASE statement also provides the capability to take action of executing different T-SQL statement based upon the outcome of different conditions.
In this tutorial, you will learn:
CASE is the extension of IF...ELSE statement. Unlike IF…ELSE, where only the maximum of one condition is allowed, CASE allows the user to apply multiple conditions to perform different sets of actions in MS SQL. Let's learn this concept in detail in the following sections.
In MS SQL, there are two types of CASE.
CASE <Case_Expression>
WHEN Value_1 THEN Statement_1
WHEN Value_2 THEN Statement_2
.
.
WHEN Value_N THEN Statement_N
[ELSE Statement_Else]
END AS [ALIAS_NAME]
Here,
Below Diagram illustrate the execution flow of Simple Case. 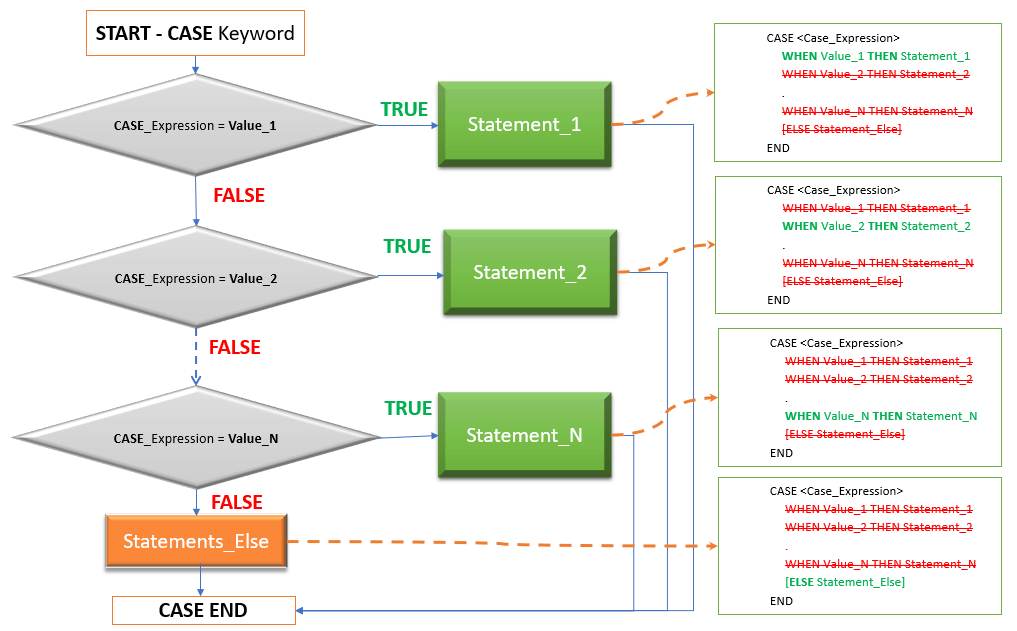
Assumption: Assume that we have the table as 'gtupapers' with two columns and four rows as displayed below:
We will use 'gtupapers' table in further examples
Query 1: SIMPLE CASE with the NO ELSE option
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE Tutorial_name WHEN 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Result: Below diagram explains the execution flow of a SIMPLE CASE with NO ELSE.
Query 2: SIMPLE CASE with the ELSE option.
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE Tutorial_name WHEN 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' ELSE 'This is NO SQL language.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Result: Below diagram explains the execution flow of a SIMPLE CASE with ELSE.
The syntax for Searched Case
CASE
WHEN <Boolean_Expression_1> THEN Statement_1
WHEN <Boolean_Expression_2> THEN Statement_2
.
.
WHEN <Boolean_Expression_N> THEN Statement_N
[ELSE Statement_Else]
END AS [ALIAS_NAME]
Here,
Below Diagram illustrate the execution flow of the Searched Case. 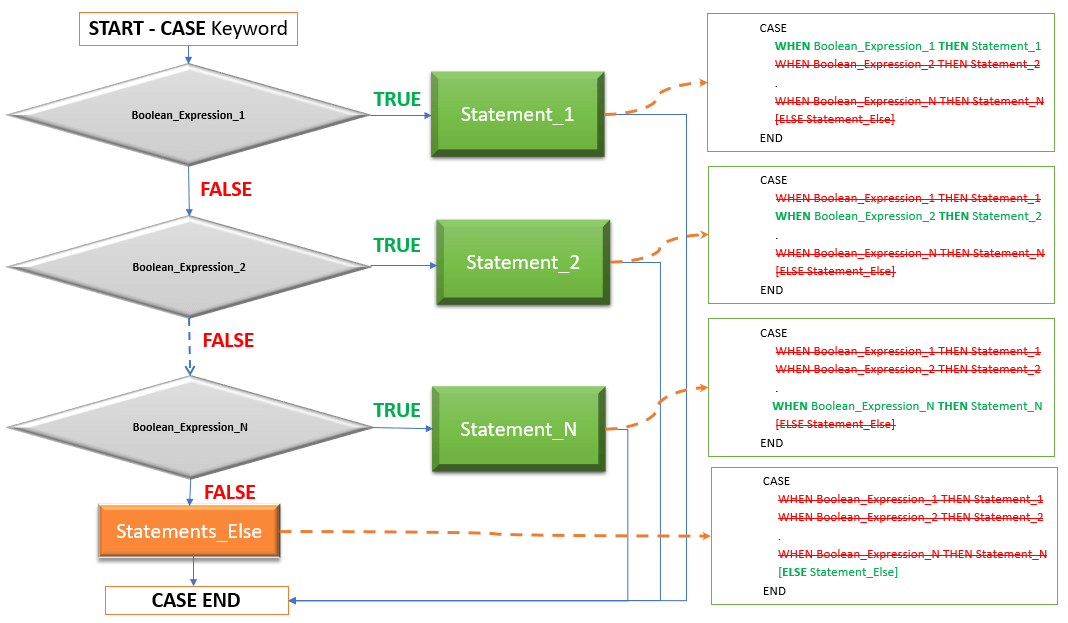
Query 1: SEARCHED CASE with the NO ELSE option
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE WHEN Tutorial_name = 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Result: Below diagram explains the execution flow of the SEARCHED CASE with NO ELSE.
Query 2: SEARCHED CASE with the ELSE option.
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE WHEN Tutorial_name = 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' ELSE 'This is NO SQL language.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Result: Below diagram explains the execution flow of the SEARCHED CASE with ELSE.
Let's have a look at SIMPLE CASE example below:
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE Tutorial_name WHEN 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' ELSE 'This is NO SQL language.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Here, 'Tutorial_name' is a part of CASE expression. Then 'Tutorial_name' value is compared with each WHEN values, i.e. 'SQL'… until 'Tutorial_name' matches with WHEN values.
On Contrary, SEARCH CASE example has no CASE Expression:
SELECT Tutorial_ID, Tutorial_name, CASE WHEN Tutorial_name = 'SQL' THEN 'SQL is developed by IBM' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'PL/SQL' THEN 'PL/SQL is developed by Oracle Corporation.' WHEN Tutorial_name = 'MS-SQL' THEN 'MS-SQL is developed by Microsoft Corporation.' END AS Description FROM gtupapers
Here, each WHEN statement has its Conditional Boolean expression. Each Boolean expression i.e. Tutorial_name = 'SQL',… is evaluated for TRUE/FALSE until first Boolean expression which evaluates to TRUE.
| Simple Case | Searched Case |
CASE keyword is immediately followed by CASE_Expression and before WHEN statement. E.g.: | Case keyword is followed by the WHEN statement, and there is no expression between CASE and WHEN. |
In Simple Case, VALUE exists for each WHEN statement. This Values: Value_1, Value_2… Are compared with single CASE_Expression sequentially. The result gets evaluate for the TRUE/FALSE condition for each WHEN Statement. | In Searched Case, Boolean_Expression exists for each WHEN statement. This Boolean_Expressions: Boolean_Expression_1, Boolean_Expression_2,… evaluates the TRUE/FALSE condition for each WHEN Statement. |
Simple Case support only equality check. I.e. whether CASE_Expression = VALUE_1, VALUE_2… E.g.: | With Boolean_Expression_N, Search Case support any operation which results in a Boolean value. It includes equal and not equal to operator. E.g.: |
We can use CASE inside IF ELSE. Below is the example MS-SQL code
DECLARE @Flight_Ticket int;
SET @Flight_Ticket = 190;
IF @Flight_Ticket > 400
PRINT 'Visit Nearby Tourist Location';
ELSE
BEGIN
SELECT
CASE
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 0 AND 100 THEN 'Visit Los Angeles'
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 101 AND 200 THEN 'Visit New York'
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 201 AND 400 THEN 'Visit Europe'
END AS Location
END
In the above example CASE is NESTED inside IF...ELSE statement:
First, IF Statement will execute and in case Condition is False then ELSE statement will execute.
Else contain Nested CASE inside it. Depending upon Flight ticket value, one amongst the following result will be displayed:
We can use CASE inside CASE. Below is the example MS-SQL code
DECLARE @Flight_Ticket int;
SET @Flight_Ticket = 250;
SELECT
CASE
WHEN @Flight_Ticket >= 400 THEN 'Visit Nearby Tourist Location.'
WHEN @Flight_Ticket < 400 THEN
CASE
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 0 AND 100 THEN 'Visit Los Angeles'
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 101 AND 200 THEN 'Visit New York'
WHEN @Flight_Ticket BETWEEN 201 AND 400 THEN 'Visit Europe'
END
END AS Location
In the above example CASE is NESTED inside another CASE statement:
The system starts with executing the outer CASE. If Flight_Ticket < $400 then inner CASE will execute.
Depending upon Flight ticket value, one amongst the following result will be displayed:
Assumption: Assume that we have the table as 'gtupapers' with two columns and four rows as displayed below:
We will use 'gtupapers' table in further examples
We can use CASE with UPDATE. Below is the example MS-SQL code:
UPDATE gtupapers SET Tutorial_Name = ( CASE WHEN Tutorial_Name = 'SQL' THEN 'Structured Query language.' WHEN Tutorial_Name = 'PL/SQL' THEN 'Oracle PL/SQL' WHEN Tutorial_Name = 'MSSQL' THEN 'Microsoft SQL.' WHEN Tutorial_Name = 'Hadoop' THEN 'Apache Hadoop.' END )
In the above example CASE is used in the UPDATE statement.
Depending upon Tutorial_Name Value, Tutorial_Name column will get the update with THEN Statement value.
Let's Query gtupapers table to check the updated value:
We can use CASE with Order By. Below is the example MS-SQL code:
Declare @Order Int; Set @Order = 1 Select * from gtupapers order by CASE WHEN @Order = 1 THEN Tutorial_ID WHEN @Order = 2 THEN Tutorial_Name END DESC
Here CASE is used with Order By.
@Order is set to 1 and as first WHEN Boolean expression evaluates to TRUE, Tutorial_ID is selected for Order by Condition
What is Exception Handling in PL/SQL? An exception occurs when the PL/SQL engine encounters an...
Download PDF 1) What is PL SQL ? PL SQL is a procedural language which has interactive SQL, as well as...
What are sub queries? A sub query is a select query that is contained inside another query. The...
What is SQLite? SQLite is an open-source, embedded, relational database management system,...
SQL stands for Structured Query Language is a domain specific programming language for managing...
What is BULK COLLECT? BULK COLLECT reduces context switches between SQL and PL/SQL engine and...