Data Warehousing
20 Best FREE Flowchart Software | Flowchart Maker (2021)
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} A flowchart is a diagram that shows the steps in a...
Multidimensional Schema is especially designed to model data warehouse systems. The schemas are designed to address the unique needs of very large databases designed for the analytical purpose (OLAP).
Types of Data Warehouse Schema:
Following are 3 chief types of multidimensional schemas each having its unique advantages.
In this tutorial, you will learn more about-
Star Schema in data warehouse, in which the center of the star can have one fact table and a number of associated dimension tables. It is known as star schema as its structure resembles a star. The Star Schema data model is the simplest type of Data Warehouse schema. It is also known as Star Join Schema and is optimized for querying large data sets.
In the following Star Schema example, the fact table is at the center which contains keys to every dimension table like Dealer_ID, Model ID, Date_ID, Product_ID, Branch_ID & other attributes like Units sold and revenue.
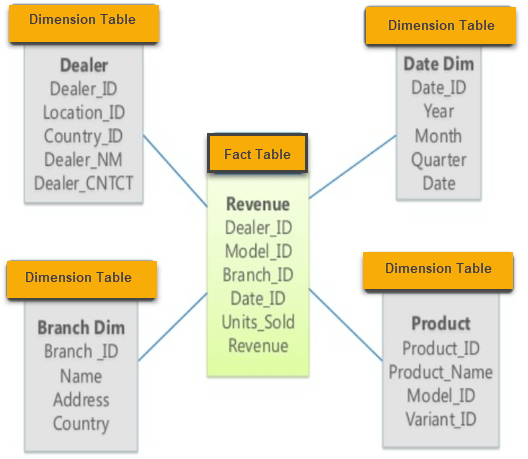
Characteristics of Star Schema:
Snowflake Schema in data warehouse is a logical arrangement of tables in a multidimensional database such that the ER diagram resembles a snowflake shape. A Snowflake Schema is an extension of a Star Schema, and it adds additional dimensions. The dimension tables are normalized which splits data into additional tables.
In the following Snowflake Schema example, Country is further normalized into an individual table.
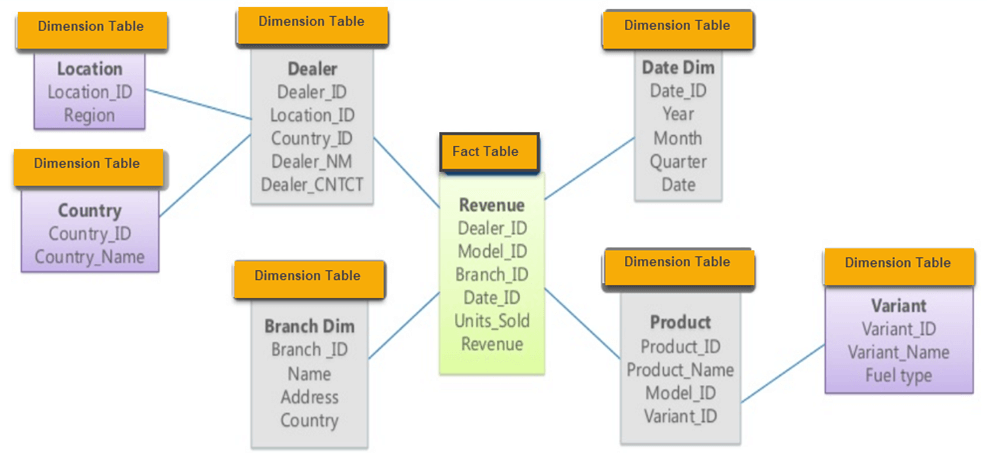
Characteristics of Snowflake Schema:
Following is a key difference between Star Schema and Snowflake Schema:
| Star Schema | Snowflake Schema |
|---|---|
| Hierarchies for the dimensions are stored in the dimensional table. | Hierarchies are divided into separate tables. |
| It contains a fact table surrounded by dimension tables. | One fact table surrounded by dimension table which are in turn surrounded by dimension table |
| In a star schema, only single join creates the relationship between the fact table and any dimension tables. | A snowflake schema requires many joins to fetch the data. |
| Simple DB Design. | Very Complex DB Design. |
| Denormalized Data structure and query also run faster. | Normalized Data Structure. |
| High level of Data redundancy | Very low-level data redundancy |
| Single Dimension table contains aggregated data. | Data Split into different Dimension Tables. |
| Cube processing is faster. | Cube processing might be slow because of the complex join. |
| Offers higher performing queries using Star Join Query Optimization. Tables may be connected with multiple dimensions. | The Snowflake schema is represented by centralized fact table which unlikely connected with multiple dimensions. |
A Galaxy Schema contains two fact table that share dimension tables between them. It is also called Fact Constellation Schema. The schema is viewed as a collection of stars hence the name Galaxy Schema.
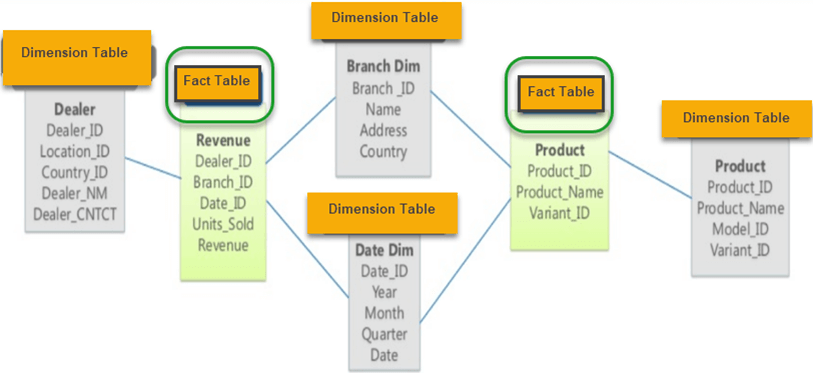
As you can see in above example, there are two facts table
In Galaxy schema shares dimensions are called Conformed Dimensions.
Characteristics of Galaxy Schema:
Snowflake schema contains fully expanded hierarchies. However, this can add complexity to the Schema and requires extra joins. On the other hand, star schema contains fully collapsed hierarchies, which may lead to redundancy. So, the best solution may be a balance between these two schemas which is Star Cluster Schema design.
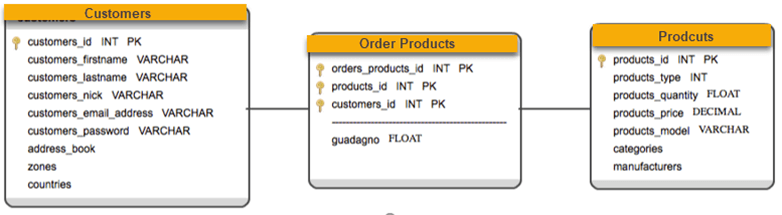
Overlapping dimensions can be found as forks in hierarchies. A fork happens when an entity acts as a parent in two different dimensional hierarchies. Fork entities then identified as classification with one-to-many relationships.
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} A flowchart is a diagram that shows the steps in a...
Log Management Software are tools that deal with a large volume of computer-generated messages. It is...
Data Warehouse Concepts The basic concept of a Data Warehouse is to facilitate a single version of...
Dimensional Modeling Dimensional Modeling (DM) is a data structure technique optimized for data...
What is Data warehouse? A data warehouse is a technique for collecting and managing data from...
What is Data Warehouse? A Data Warehouse collects and manages data from varied sources to provide...