Linux
Linux Tutorial PDF for Beginners: Basics Guide (FREE Download)
$20.20 $9.99 for today 4.5 (119 ratings) Key Highlights of Linux Tutorial PDF 186+ pages eBook...
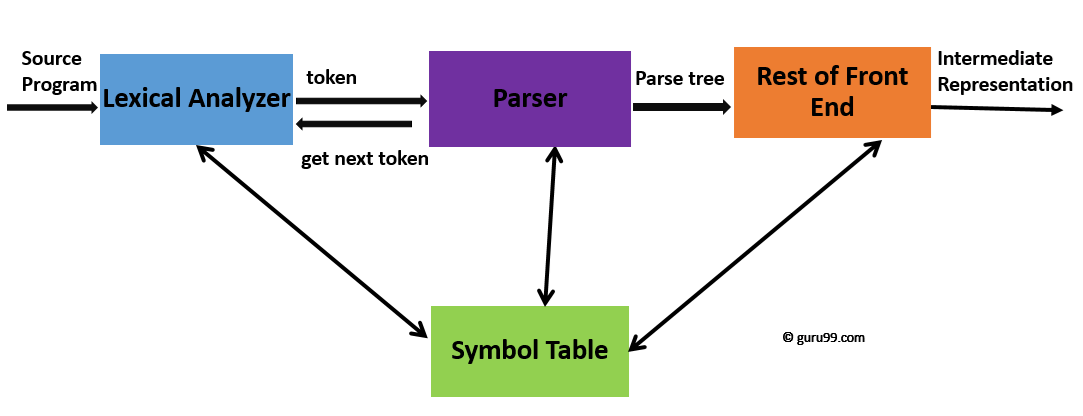
Syntax Analysis is a second phase of the compiler design process in which the given input string is checked for the confirmation of rules and structure of the formal grammar. It analyses the syntactical structure and checks if the given input is in the correct syntax of the programming language or not.
Syntax Analysis in Compiler Design process comes after the Lexical analysis phase. It is also known as the Parse Tree or Syntax Tree. The Parse Tree is developed with the help of pre-defined grammar of the language. The syntax analyser also checks whether a given program fulfills the rules implied by a context-free grammar. If it satisfies, the parser then creates the parse tree of that source program. Otherwise, it will display error messages.
In this tutorial, you will learn
Important terminologies used in syntax analysis process:
A parse also checks that the input string is well-formed, and if not, reject it.
Following are important tasks perform by the parser in compiler design:
Parsing techniques are divided into two different groups:
In the top-down parsing construction of the parse tree starts at the root and then proceeds towards the leaves.
Two types of Top-down parsing are:
Predictive parse can predict which production should be used to replace the specific input string. The predictive parser uses look-ahead point, which points towards next input symbols. Backtracking is not an issue with this parsing technique. It is known as LL(1) Parser
This parsing technique recursively parses the input to make a prase tree. It consists of several small functions, one for each nonterminal in the grammar.
In the bottom up parsing in compiler design, the construction of the parse tree starts with the leave, and then it processes towards its root. It is also called as shift-reduce parsing. This type of parsing in compiler design is created with the help of using some software tools.
Common Errors that occur in Parsing in System Software
A parser should able to detect and report any error found in the program. So, whenever an error occurred the parser. It should be able to handle it and carry on parsing the remaining input. A program can have following types of errors at various compilation process stages. There are five common error-recovery methods which can be implemented in the parser
A grammar is a set of structural rules which describe a language. Grammars assign structure to any sentence. This term also refers to the study of these rules, and this file includes morphology, phonology, and syntax. It is capable of describing many, of the syntax of programming languages.
Rules of Form Grammar
Notational conventions symbol may be indicated by enclosing the element in square brackets. It is an arbitrary sequence of instances of the element which can be indicated by enclosing the element in braces followed by an asterisk symbol, { ... }*.
It is a choice of the alternative which may use the symbol within the single rule. It may be enclosed by parenthesis ([,] ) when needed.
Two types of Notational conventions area Terminal and Non-terminals
1.Terminals:
2.Nonterminals:
A CFG is a left-recursive grammar that has at least one production of the type. The rules in a context-free grammar are mainly recursive. A syntax analyser checks that specific program satisfies all the rules of Context-free grammar or not. If it does meet, these rules syntax analysers may create a parse tree for that programme.
expression -> expression -+ term expression -> expression – term expression-> term term -> term * factor term -> expression/ factor term -> factor factor factor -> ( expression ) factor -> id
Grammar derivation is a sequence of grammar rule which transforms the start symbol into the string. A derivation proves that the string belongs to the grammar's language.
Left-most Derivation
When the sentential form of input is scanned and replaced in left to right sequence, it is known as left-most derivation. The sentential form which is derived by the left-most derivation is called the left-sentential form.
Right-most Derivation
Rightmost derivation scan and replace the input with production rules, from right to left, sequence. It's known as right-most derivation. The sentential form which is derived from the rightmost derivation is known as right-sentential form.
Syntax Analyser | Lexical Analyser |
The syntax analyser mainly deals with recursive constructs of the language. | The lexical analyser eases the task of the syntax analyser. |
The syntax analyser works on tokens in a source program to recognize meaningful structures in the programming language. | The lexical analyser recognizes the token in a source program. |
It receives inputs, in the form of tokens, from lexical analysers. | It is responsible for the validity of a token supplied by the syntax analyser |
$20.20 $9.99 for today 4.5 (119 ratings) Key Highlights of Linux Tutorial PDF 186+ pages eBook...
Torrent client is a software for downloading files that utilize a peer to peer system. This...
What are Linux Regular Expressions? Linux Regular Expressions are special characters which help...
What is SAS? SAS stands for S tatistical A nalysis S oftware which is used for Data Analytics. It helps...
Introduction to Data Analysis Data analysis can be divided into three parts Extraction: First, we...
Who is a Software Developer? Software developers are professional who builds software which runs...