Ethical Hacking
Kali Linux Tutorial for Beginners: What is, How to Install & Use
What is Kali Linux? Kali Linux is a security distribution of Linux derived from Debian and...
A VLAN is a custom network that is created from one or more Local Area Networks. It allows a group of devices available in multiple networks to be combined into one logical network. The result becomes a virtual LAN that is administered like a physical LAN. The full form of VLAN is Virtual Local Area Network.
In this Networking tutorial, you will learn:
VTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol is used to exchange VLAN information. This type of protocol was developed to effectively manage the transfer of frames from different VLANs on a single physical line. The full form of VTP is the VLAN Trucking Protocol.
Using VTP, you can synchronize VLAN information (like VLAN name or VLAN ID) with switches into the same VTP domain.
For example, let us consider a large size network with 100 switches. Without VTP protocol, if you try to create a VLAN on each Switch, you need to enter VLAN configuration commands on every Switch!
Trunking protocol VTP allows you to create the VLAN only on a single switch. Similarly, if you want to delete a VLAN, you only require deleting it in one switch. After that, it will automatically circulate to every other switch inside the same VTP domain.
Two important VTP technique are:
Here are some requirements for VTP to communicate VLAN information between CISCO switches.
Here are some important Components of VTP
VTP domain limits the extent to which configuration change are propagated in the network if an error occurs. At a time switch can be a member of only one VTP domain at a time. Until the VTP domain name is specified, you can't create or modify VLANs on a VTP server mode. VLAN information is not propagated over the network. This component consists of single or multiple interconnected switches.
This component prevents unnecessary flooding of broadcast information from one VLAN across all trunks in the VTP domain. It allows pruning on one VTP server switch in one domain is disabled by default. It is enabled by using the VTP pruning global configuration command.
This VTP mode uses a hierarchy of advertisements to synchronize and distribute VLAN configurations in the network. This component distributes VTP domain name and VLAN configurator changes to VTP-enabled switches.
Whenever a request for advertisement needs to be sent to a VTP server in the same VTP domain, at that time VTP server responds by sending a summary advertisement and then a subset advertisement.
Request advertisement are sent when:
This type of advertisement component contains the VTP domain name, the current revision number, and other VTP configuration details.
A subset of advertisements contains VLAN information:
You can configure Switch in three modes: 1) Server, 2) Client, or 3) Transparent.
| VTP Server | VTP Client | VTP Transparent | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Create/Modify/Delete VLANs | Yes | No | Only local |
| Synchronizes itself | Yes | Yes | No |
| Forwards advertisements | Yes | Yes | Yes |
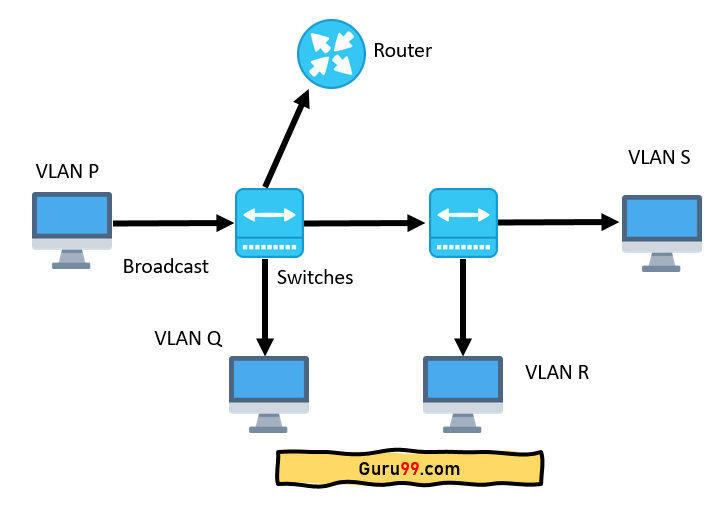
In the diagram above, you can see each switch has two VLANs.
Step 1) On the first switch, VLAN P and VLAN Q are sent through a single port (trunked) to the router and another port to the second switch.
Step 2) VLAN R and VLAN S are trunked from the second switch to the first switch and then the router's first switch. This trunk can carry traffic from all four VLANs connections.
Step 3) The trunk link from the first switch to the router should be carried to all four VLANs.
Step 4) VLAN P that needs to get to a computer on VLAN Q (or VLAN R or VLAN S) must travel from the switch to the router and return to the switch.
Here are the important pros/benefits of VTP:
Here are some important VTP Configuration Guidelines
Three types of VTP versions are V1, V2, and V3.
Among the first two versions are similar except that V2 adds support for token ring VLANs.
V3 adds the following features:
What is Kali Linux? Kali Linux is a security distribution of Linux derived from Debian and...
Wireshark is a widely used network monitoring and WiFi troubleshooting tool. However, with...
{loadposition top-ads-automation-testing-tools} China has placed numerous restrictions on...
Anti-spyware removes malicious spyware and protects your computer system. They detect and remove...
Wireless networks are accessible to anyone within the router’s transmission radius. This makes...
What is CISSP? CISSP- full form Certified Information Systems Security Professional is considered as a...